The Identity underground report | Silverfort
Cyber Security |
Your defenses are sky high…
We can monitor and safeguard what’s visible above ground, but our knowledge is limited. Below the surface lies an unseen world of misconfigurations, forgotten accounts, and vulnerabilities—Identity Threat Exposures (ITEs). Attackers exploit these for credential theft and more, posing significant risks to security. This report delves into these underground threats and their implications.
Report Highlights
- 67% of organizations have left their SaaS apps vulnerable by syncing insecure on-prem passwords.
- 37% of admins use NTLM authentication, risking exposure of clear text passwords.
- 31% of users are high-privilege service accounts with low visibility.
- 13% of accounts are inactive, providing attackers an avenue to compromise without detection.
- On average, a single AD misconfiguration introduces 109 new shadow admins, facilitating password resets.
- 7% of users wield admin-level access without belonging to any admin group.
- Legacy NTLMv1 is used by 7% of admin users, risking password exposure.
- 12% of admin accounts are configured for unconstrained delegation, opening doors to privilege escalation attacks.
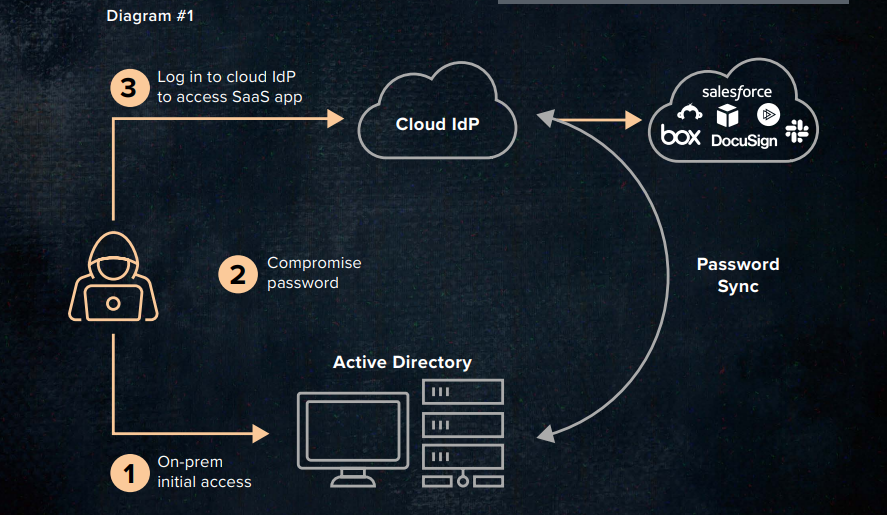
The attack path from underground to the cloud
The prevailing approach among organizations is the adoption of a hybrid identity infrastructure, combining Active Directory (AD) for on-premises resources and a cloud Identity Provider (IdP) for Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions. Typically, AD synchronizes user hashes with the cloud IdP, allowing users to utilize the same credentials for both on-premises and cloud-based applications. However, this practice significantly expands the potential attack surface of the SaaS environment.
Any vulnerability that leads to the exposure of cleartext passwords grants attackers direct access to cloud assets. Therefore, Identity Threat Exposures (ITEs) facilitating access to cleartext passwords pose a grave risk, including weaknesses in password encryption (such as NTLM, NTLMv1, and admins with SPN) or enabling password resets (like shadow admins), which are frequently exploited by adversaries.

Executive Summary
Crucial segments of your identity’s vulnerability landscape remain obscured, undefended, and concealed underground. This report marks the initial endeavor to chart the most vital weaknesses in identity security within the hybrid enterprise setup. These Identity Threat Exposures (ITEs), compiled from extensive observations across numerous live production environments, represent the pivotal vulnerabilities exploited by attackers to obtain credentials, elevate privileges, and traverse networks, both on-premises and in the cloud. They persist as formidable challenges to mitigate, arising from misconfigurations, legacy systems, or inherent platform features.
Misconfigurations are an inherent aspect of large-scale production environments, while legacy systems are often indispensable for applications and systems resistant to migration or modernization. Additionally, inherent platform features remain immutable realities. The ITEs delineated herein underpin the marked surge in lateral movement, now an inherent characteristic of nearly every cyberattack.
Despite this, a comprehensive understanding of the resilience of the identity vulnerability landscape has yet to be integrated into the security team’s protocols. It is our aspiration that armed with the insights from this report, security teams can now illuminate critical weaknesses and undertake proactive measures to address them.
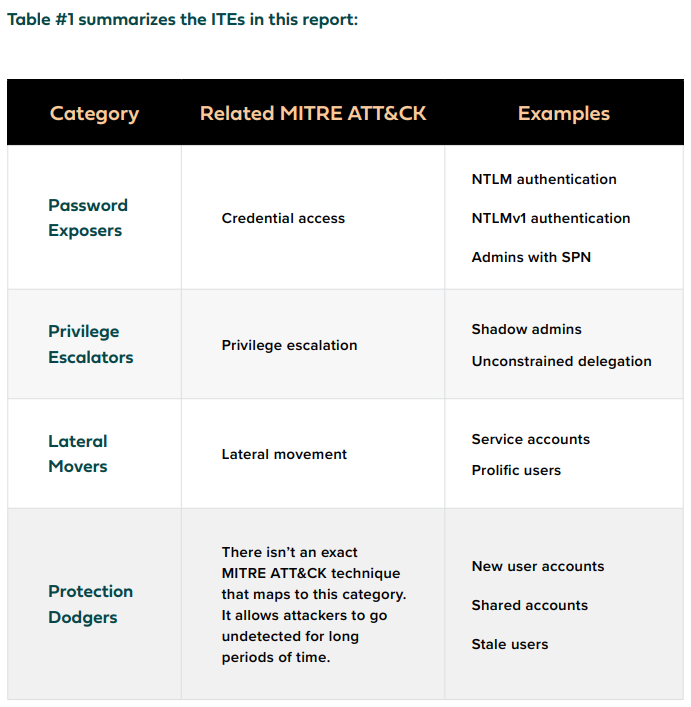
Introducing Identity Threat Exposures (ITEs)
What exactly constitutes Identity Threat Exposures (ITEs)?
ITEs represent security vulnerabilities that expose an environment to identity-related threats such as credential theft, privilege escalation, or lateral movement. These vulnerabilities can stem from misconfigurations, malpractices, outdated identity infrastructure, or inherent system features.
In this report, we focus on ITEs that are widespread, impactful, and readily exploitable by attackers. To ensure relevance across organizations, we’ve applied specific inclusion criteria:
- Prevalence: The ITE must be prevalent in a significant portion of the assessed environments, indicating its widespread occurrence.
- Accessibility: The ITE should be easily discoverable by adversaries who have gained initial access to the targeted environment.
- Impact: The ITE should significantly facilitate adversary access to systems and resources, privilege escalation, or lateral movement.
Each ITE is detailed with the following attributes:
- MITRE mapping: The specific MITRE technique associated with the ITE.
- Type: The underlying cause of the ITE, categorized as misconfiguration, legacy infrastructure, or inherent platform feature.
- Compromise impact: The potential consequences of an attacker exploiting the ITE.
- Accessibility: How an attacker can identify and leverage the existence of the ITE.
- Visibility and protection: The effectiveness of existing security measures in mitigating the risk posed by the ITE.
What ITE types are there?
We categorize ITEs into four distinct groups, depending on the outcomes attackers can accomplish when exploiting them:
1. Password Exposers:
These ITEs facilitate adversaries in accessing a user account’s cleartext password.
2. Privilege Escalators:
These ITEs empower adversaries to escalate the access privileges they already hold.
3. Lateral Movers:
These ITEs enable adversaries to execute undetected lateral movement using compromised accounts.
4. Protection Dodgers:
These ITEs diminish the effectiveness of security controls in monitoring and safeguarding user accounts.
Continue your journey into identity security. Download the full report now for comprehensive insights and actionable strategies to safeguard your organization against identity threats.
The Table of Contents of “The Identity underground report” Report :
- Executive Summary
- Introducing Identity Threat Exposures (ITEs)
- Password Exposers
- Privilege Escalators
- Lateral Movers
- Protection Dodgers
- Recommendations
Number of Pages:
- 34 pages
Pricing:
- Free






